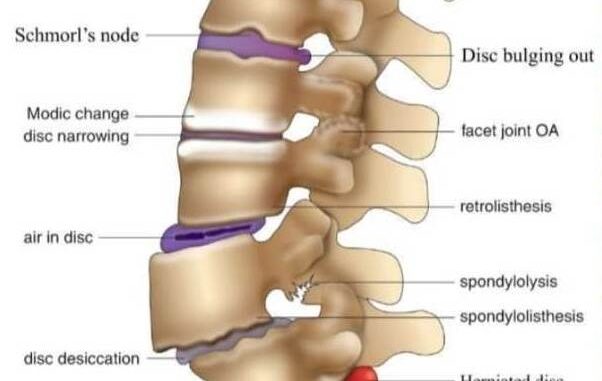
Disc bulging
Disc bulging, a common spinal condition, occurs when the outer layer of a spinal disc weakens, allowing the inner gel-like substance to protrude outward. This can lead to discomfort, pain, and sometimes, nerve compression. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of disc bulging is essential for effective treatment.
Causes:
Disc bulging often results from age-related wear and tear on the spinal discs. However, it can also be caused by sudden trauma or injury to the spine. Factors such as poor posture, repetitive heavy lifting, obesity, and genetic predisposition can contribute to its development.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of disc bulging vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Common signs include localized pain, stiffness, numbness, tingling sensations, and weakness in the affected area. In some cases, disc bulging may compress nearby nerves, leading to radiating pain, known as sciatica, which can extend into the buttocks, legs, or feet.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing disc bulging typically involves a thorough physical examination and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans. These imaging techniques help healthcare providers visualize the extent of disc protrusion and assess its impact on surrounding structures.
Management:
Treatment for disc bulging aims to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage. Conservative management options include:
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches can strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and promote proper alignment.
Pain Management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and corticosteroid injections may help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with disc bulging.
Chiropractic Care: Spinal manipulation and adjustments performed by chiropractors can relieve pressure on affected discs and improve spinal function.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting ergonomic practices, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help prevent further strain on the spine.
In severe cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered to decompress nerves and stabilize the spine.
In conclusion, understanding the causes, symptoms, and management options for disc bulging is crucial for individuals experiencing spinal discomfort. Early intervention and a comprehensive treatment approach can improve outcomes and enhance quality of life. If you suspect disc bulging or are experiencing persistent back pain, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.




Be the first to comment